McClung and Broeren watched the SLS launch and monitored the mission from the ULA facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station next to Kennedy Space Center. McClung, “a third-generation space guy,” said he was thinking of his grandfather, who took part in developing the Surveyor I spacecraft that landed on the moon in 1966, and his father, who helped train Apollo astronauts before taking on project management for the space shuttle.
“Dad and I still talk a lot of shop about the space program,” McClung said. “He’s excited about Artemis I and excited for me.”
With their mission accomplished, the integrated ICPS and Orion stage adapter are moving into a solar orbit far from Earth and its moon. For the Artemis II and III missions — when ULA-built upper stages will boost Orion spacecraft with astronauts onboard — NASA will assess opportunities to deploy more CubeSats.
Meanwhile, Boeing teams are building an even more powerful Exploration Upper Stage. It will provide in-space boosts for Artemis IV and beyond.
Visit Boeing’s Artemis I website for more information on the mission and the rocket. Follow @BoeingSpace for ongoing mission highlights and @Spectrolab_Inc for details on the secondary payloads powered by company technology.
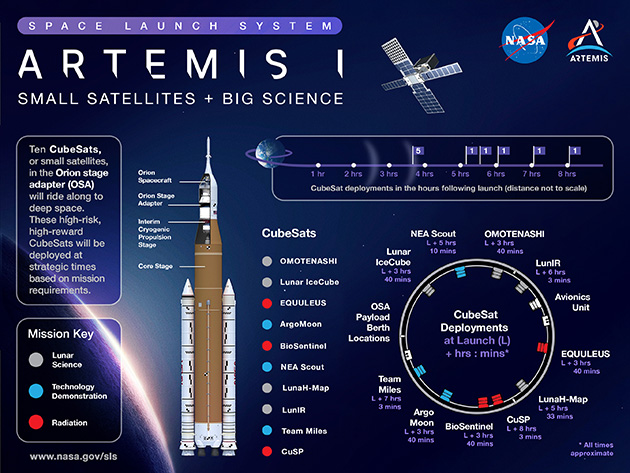
Artemis I CubeSat payloads powered by Spectrolab solar cells:
BioSentinel
|
NASA Ames experiment will use single-celled yeast to detect, measure and compare the impact of deep-space radiation on living organisms.
|
CuSP
|
Southwest Research Institute experiment will measure the sun’s particles and magnetic fields as a space weather station.
|
EQUULEUS
|
The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency and the University of Tokyo will image Earth’s radiation environment.
|
LunaH-Map
|
Arizona State University experiment will use neutron spectrometers to create high-fidelity maps of near-surface hydrogen at the moon’s south pole.
|
Lunar Ice Cube
|
Morehead State University experiment will search for water and other volatile materials on and around the moon with an infrared spectrometer.
|
NEA Scout
|
NASA Marshall demonstration will travel via solar sail to an asteroid and take images of its surface.
|
Other Artemis I CubeSat payloads:
ArgoMoon
|
A European Space Agency observation of the ICPS with advanced optics and a software imaging system.
|
LunIR
|
Lockheed Martin mission will gather advanced infrared images of the lunar surface.
|
OMOTENASHI
|
The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency will attempt to put the world’s smallest lunar lander on the moon’s surface to study its environment.
|
Team Miles
|
A one-year demonstration of advanced smallsat operations using plasma thrusters. A team of citizen scientists and engineers won its spot on Artemis I through a NASA competition.
|