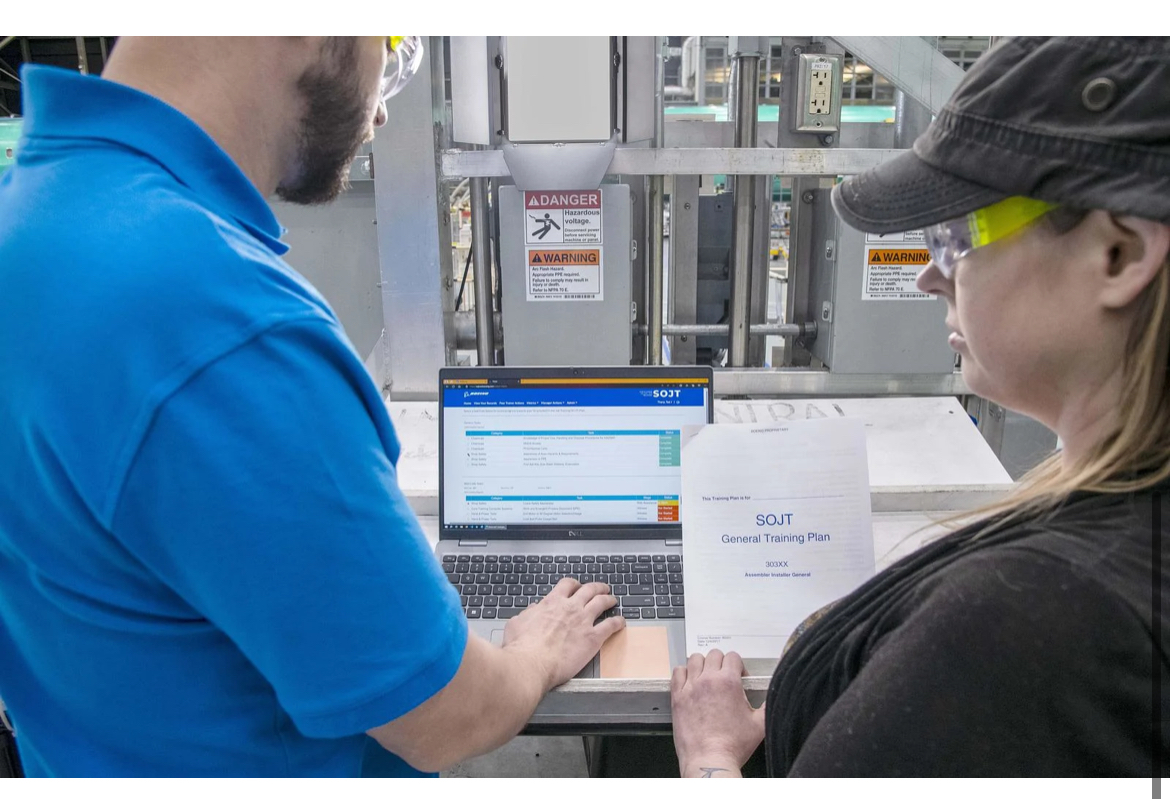
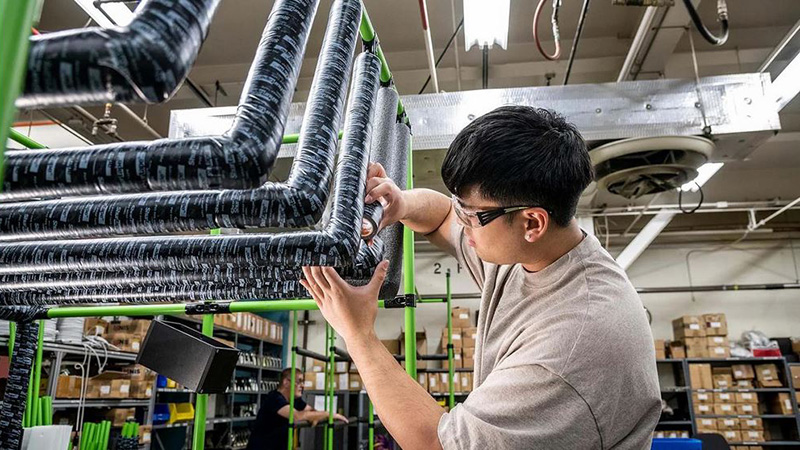
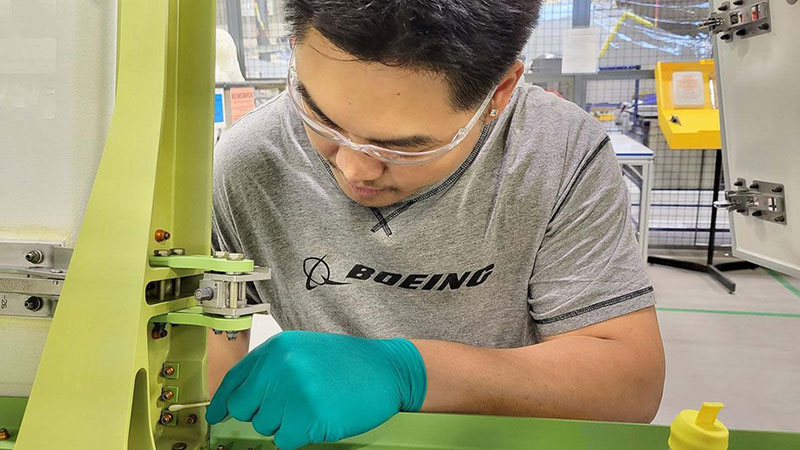
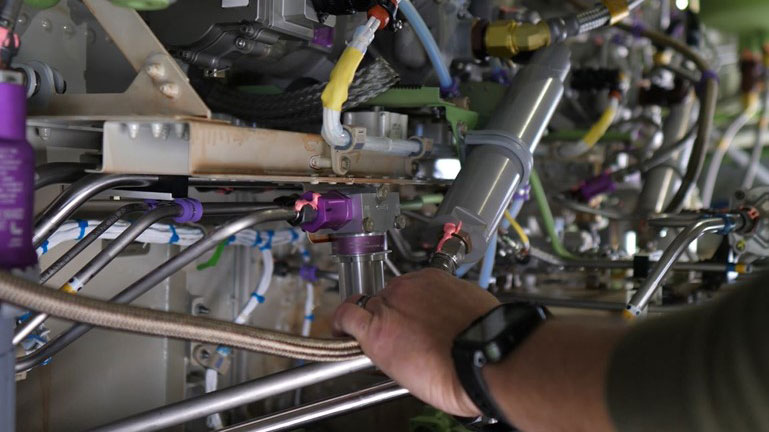
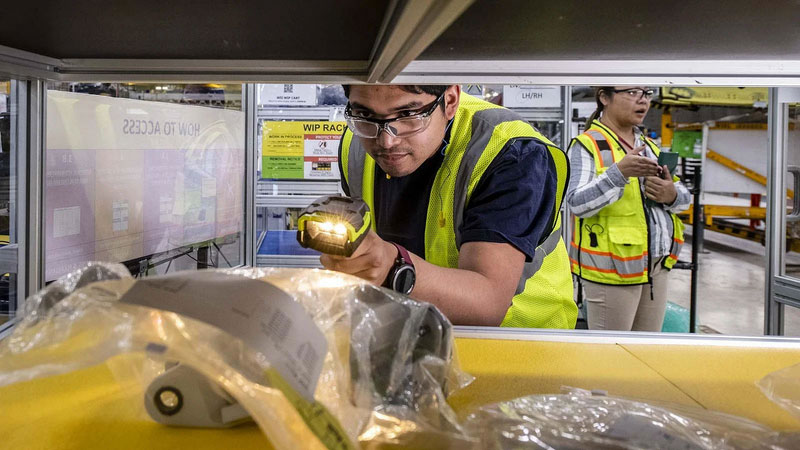
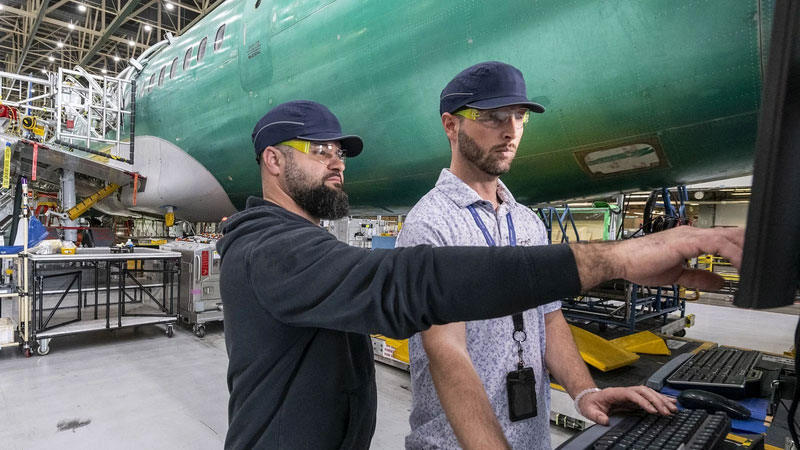
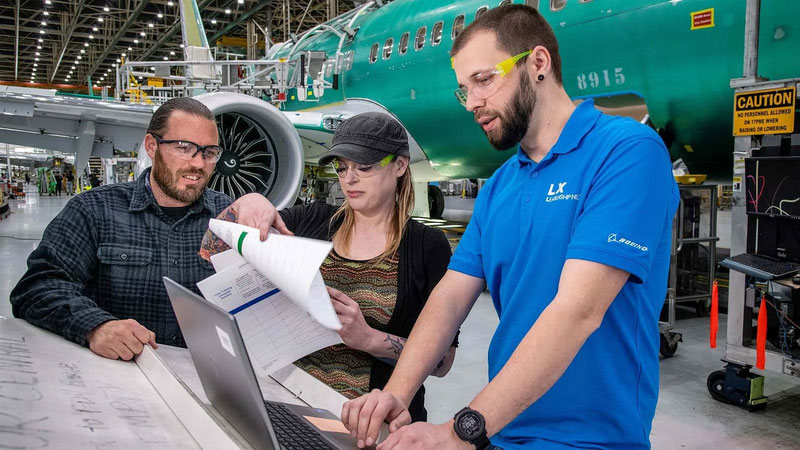
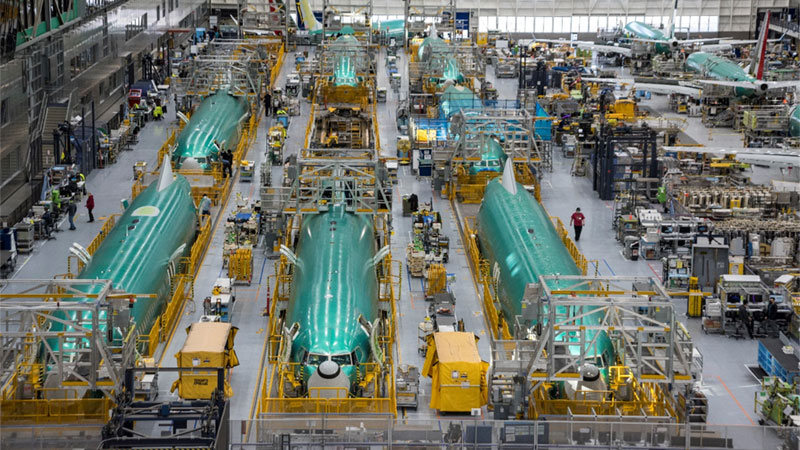
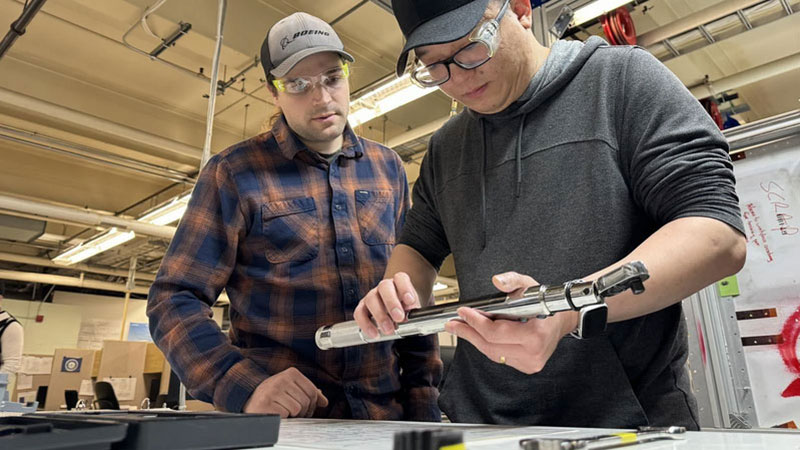
Boeing took immediate action in January 2024 to ensure the safety of our fleet and production operations for all of our airplanes.
Then, we gathered feedback from our employees, regulator, customers and independent experts to develop a comprehensive plan that strengthens our safety management, quality assurance and safety culture across our production systems.
Boeing’s Safety & Quality Plan generally aligns to four focus areas: investing in workforce training, simplifying plans and processes, eliminating defects, and elevating our safety and quality culture. The plan also sets forth measures to continuously monitor and manage the health of our production system.
We are committed to this plan and to continuous improvement, which has helped make commercial aviation the safest mode of transportation.